
What are Mutual Funds? | Asset Classes
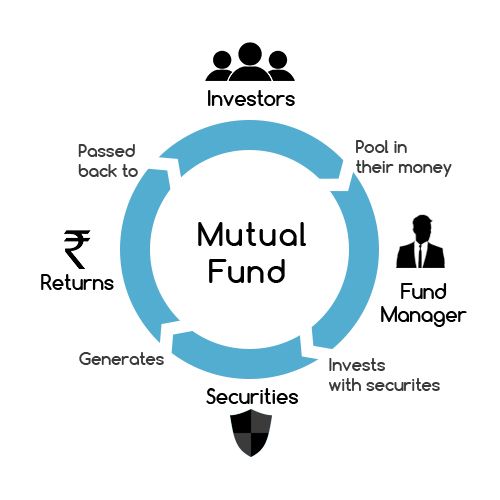
Mutual funds are a pool of money, which is poured by a large number of investors with expectations of getting good interest. These funds are then used by Fund Managers to invest in various asset classes (depending on the type of fund) so that they can fulfill the expectations of investors.
Personally, I think I would be better to start with the basics. You can read about bank and FD accounts here if you an absolute beginner. Get excited financial world is amazing.
Why mutual funds came into existence?
Mutual Funds are based on the idea of “Make Your Money Work”. So, what happens when our money starts working? It actually starts generating more money.
Mutual funds are not the only way to make your money work. Other options are also available. The money will start generating more money, automatically, if you invest it even yourself, i.e. suppose you have $1000 then you can start a small shop with that amount and if you are a good shopkeeper then your shop will grow. This way, your $1000 investment will start growing.
But, it seems like a heck lot of job to open a store & then do all those things just to make your $1000 grow. This is the reason mutual funds basically came into existence.
These funds allow a large number of small investors to deposit money with them. Then, the fund house (which ensures the proper functioning of mutual fund) appoints a professional fund manager who takes all the investment decisions for you and then provides a return.
Types of Mutual Funds
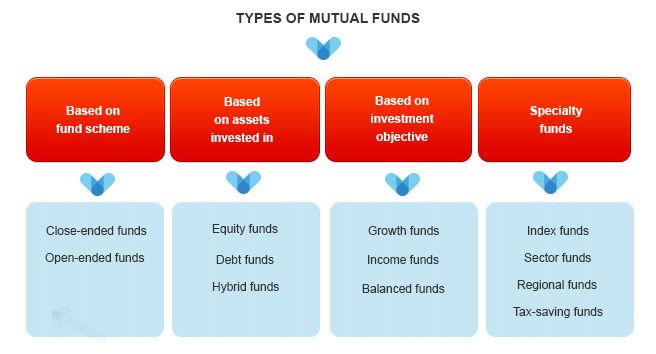
There are many categories of funds available in the market. A single mutual fund can fall into various categories.
On the basis of assets there are basically three types of mutual funds:
- Equity Funds: These funds invest in stocks of various companies. The return of this category can be very high depending upon the price of stocks. The risk is also comparatively high because of various reasons.
- Debt Funds: These funds invest in debt instruments. The return of this category is just around Fixed Deposit but they provide additional benefits. The risk is low in liquid and short term debt funds.
- Hybrid Funds: These funds actually invest in a mix of equity and debt assets. They give a medium return and also expose the invested money to medium risk.
On the basis of investment objective:
- Growth Funds: In these funds, all the dividends and interest are reinvested to let the compound interest show its magic. These are ideal for long term investors.
- Income Funds: These funds regularly provides back dividends and interest to the investor like the income. These are ideal for retired people.
On the basis of Management:
- Active Funds: These funds are actively managed by a fund manager. All the investment decisions depend upon his guidance and knowledge. They charge a high expense ratio.
- Passive Funds: These funds are also called Index Funds. They simply track an index like Nifty 50, Sensex 30, etc. So, they don’t need an active fund manager. That’s why they have a lower expense ratio.
Hot Read: Why I am an Atheist? | A Logical Explanation
Expense Ratio
Fund Houses for mutual funds are similar to what banks are for savings accounts. Both of them are big organizations which have expenses like any other company.
In the case of fund houses, the expenses are funded by expense ratio charged on the money deposited in the mutual funds. Suppose you invest $1000 dollars in an Equity Fund having a 2% expense ratio.
If in a year, it gives a gross 20% return then you will get 18% only after deducting 2% expense ratio. So, if the fund gave $200 returns then you will get only $180 because the expense ratio is also deducted beforehand.
Equity Funds usually have more expense ratio as compared to Debt Funds and Active Funds also charge more than Passive Funds.
In the case of banks, you never get to know in detail about the way your money is being used. The bank simply manages all this on its own and promises you a fixed rate of interest.
But, mutual funds are a lot more transparent in the regard that they need to share all the details with investors. Mutual funds are similar to an FD as it gives some interest and differs from the FD if we consider the rate of interest.
Net Asset Value (NAV)
After you deposit the money in the mutual fund, the fund manager invests it into various assets. You indirectly own some part of those assets. Suppose, if your fund is an equity fund. Then, you will own a number of stocks on the basis of your investment amount.
In reality, on a working day, the value of these stocks keeps changing every minute. But, mutual funds are valued only once a day to keep the matter simple. So, to enforce this, the concept Net Asset Value (NAV) is used.
Generally, at the end of each day, your fund house will calculate the NAV on the basis of closing prices of assets it had invested its money. I think this much is enough to get you through the basics of mutual funds.
Investing in mutual funds won’t really be effective without proper financial planning. I insist you plan your financial goals first.



This Post Has 0 Comments